❓How to Calculate the Cost of Opening a USDⓈ-M Perpetual Futures Contract Position
Calculating the cost of opening a Limit Order:
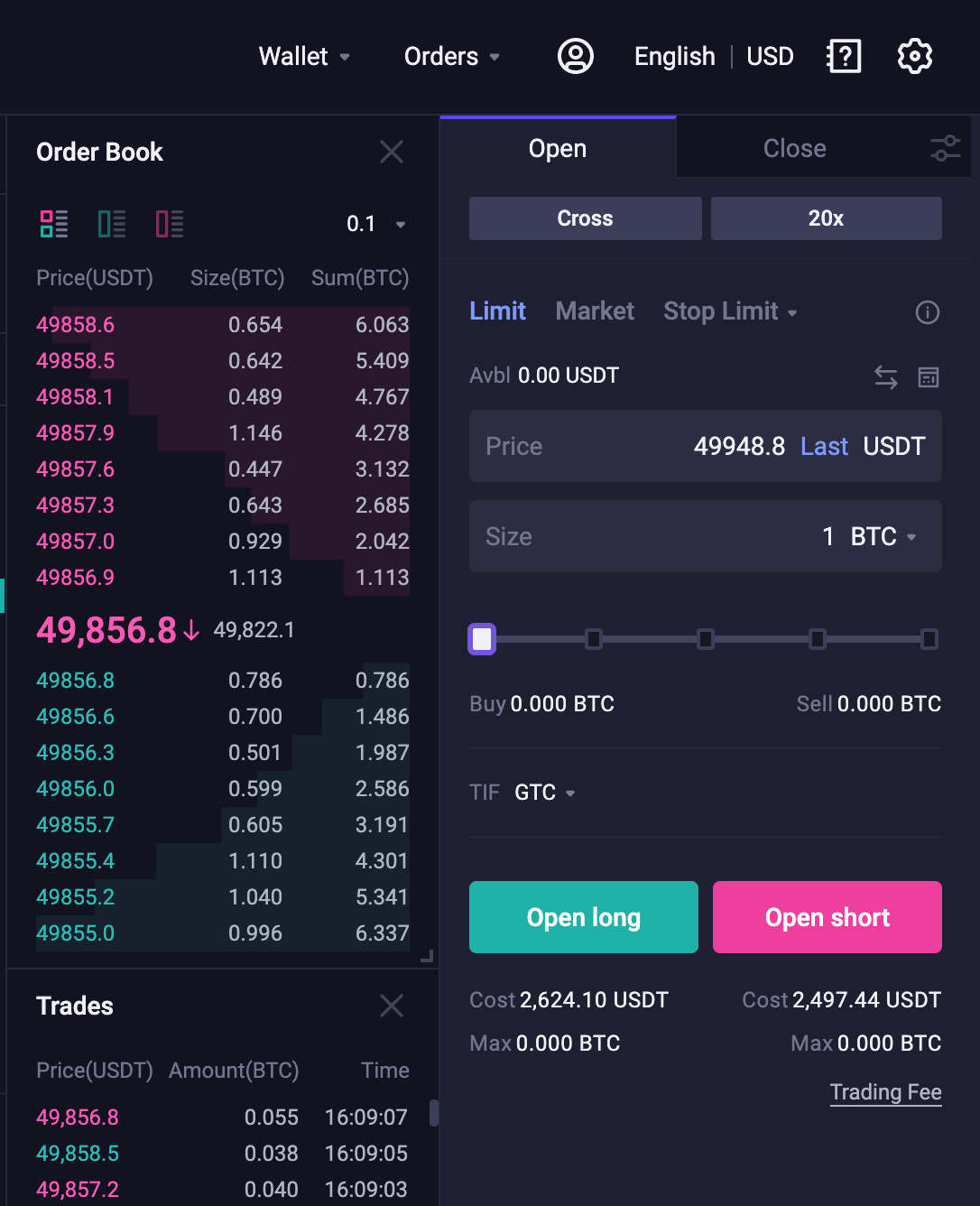
1. Calculate the Initial Margin
Initial Margin
= Notional Value / Leverage Multiplier
=(49948.8*1 BTC)/20x
=2497.44
2. Calculate Open Loss
Open Loss = Number of Contracts × Absolute Value {min [0, Order Direction × (Mark Price — Order Price)]}
Direction of order: 1 for long order;-1 for short order
Open Loss of long order
= Number of Contract * Absolute Value {min[0, Direction of order * (Mark price — Order Price)]}
= 1 * Absolute Value {min[0, 1 * (49822.1- 49948.8)]}
= 1 * Absolute Value {min[0, (-126.7)]}
= 1 * 126.7
= 126.7
Open loss occurs when you place a long order.
Open Loss of Short Order
= Number of Contract * Absolute Value {min[0, Direction of order * (Mark Price — Order Price)]}
= 1 * Absolute Value {min[0, -1 * (49822.1- 49948.8)]}
= 1 * Absolute Value {min[0, 126.7]}
= 1 * 0
= 0
Open loss does not occur when you place a Short order.
3. Calculate the cost of Opening a Position
Since there is no Open Loss when you place a Short order, the cost of opening a Short order is equal to the Initial Margin.
Cost of opening a Long Order
=2497.44 + 126.7
=2624.14
Cost of opening a Short Order =2497.44 + 0 =2497.44
Since an Open Loss occurs when you place a Long order, it costs more to place a Long order. In addition to the Initial Margin, you must also take into account the Open Loss.
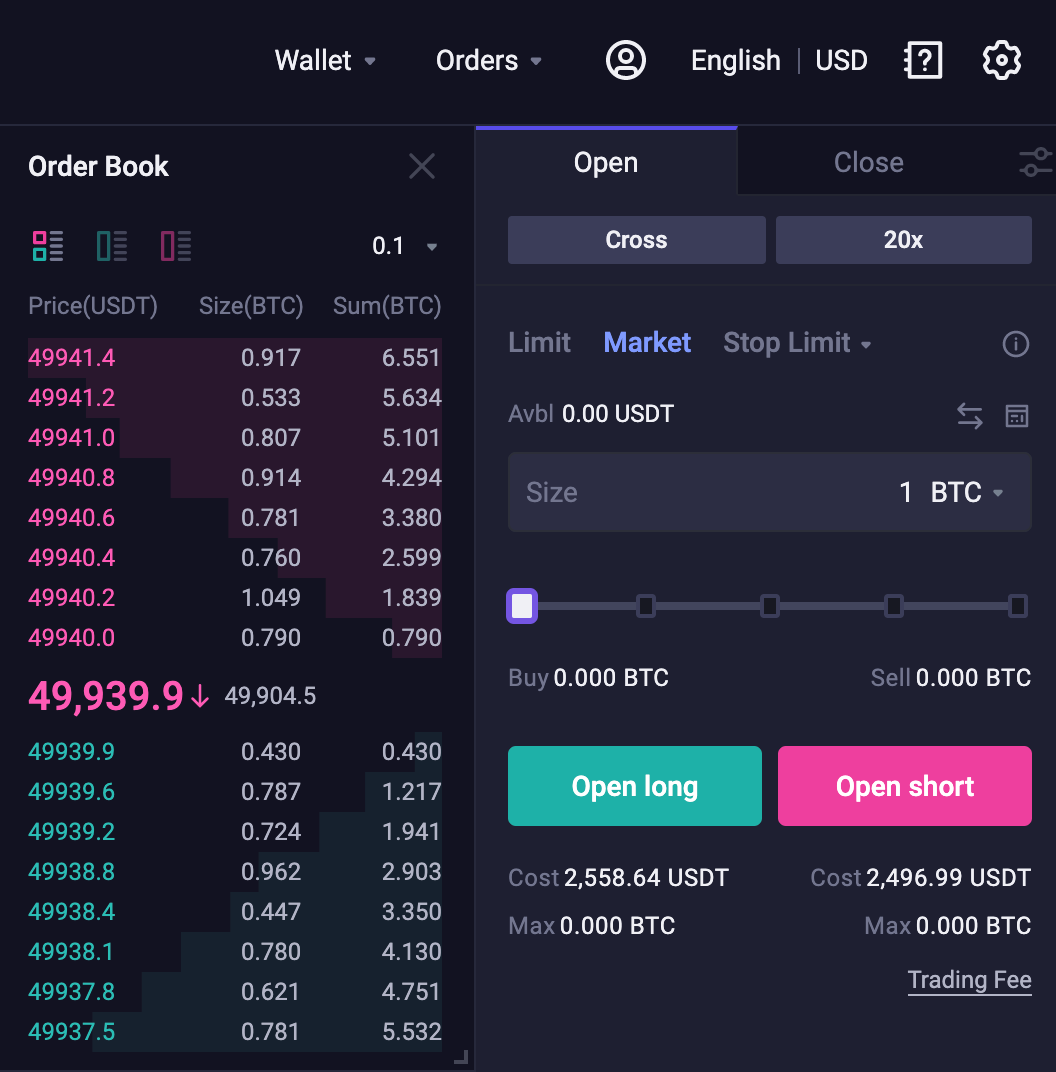
Calculating the cost of opening a Market Order:
1. Calculate Estimated Entry Price
Long order estimated entry price = ask[0] * (1 + 0.05%); Short order estimated entry price = max(bid[0], mark price)
Estimated entry price of long order
=ask[0]*(1 + 0.05%)
=49939.9*(1 + 0.05%)
=49964.87
*[0]:Level 1 price
Assuming price of short order
= max(bid[0], mark price)
= max (49940, 49904.5)
= 49940
*[0]:Level 1 price
2. Calculate the Initial Margin
Initial Margin = Notional Value / Leverage Multiplier
Initial margin for long order
= Estimated entry price of long order * Number of Contracts / Leverage Multiplier
=49964.87 * 1 /20
=2498.2435
Initial margin for short order
= Estimated entry price of short order * Number of Contracts / Leverage Multiplier
=49940 * 1/20
=2497
3. Calculate the Open Loss
Open Loss = Number of Contract * Absolute Value {min[0, direction of order * (mark price — order price)]}
Direction of order: 1 for long order;-1 for short order
Open loss for long order
= Number of Contract * Absolute Value {min[0, direction of order * (mark price — order price)]}
= 1 * Absolute Value {min[0, 1 * (49904.5–49964.87)]}
= 1 * Absolute Value {min[0, -60.37]}
= 1 * 60.37
= 60.37
An Open Loss occurs when you place a Long order.
Open loss for short order
= Number of Contract * Absolute Value {min[0, direction of order * (mark price — order price)]}
= 1 * Absolute Value {min[0, -1 * (49904.5–49940)]}
= 1 * Absolute Value {min[0, 35.5]}
= 1 * 0
= 0
An Open Loss does not occur when you place a Short order.
4. Calculating the cost of Opening a Position
Since Open Loss occurs when you place a Long order, it costs more to place a Long order. In addition to the Initial Margin, you must also take into account the Open Loss.
Cost of opening a Long Order
=2498.2435+60.37
=2558.6135
Cost of opening a Short Order
=2497+0
=2497
Since there is no Open Loss when you place a short order, the cost of opening a Short order is equal to the Initial Margin.
Last updated